
Vault Server Installation
Before you install Vault, review this Installation Guide to learn how the Vault installer works and what is needed for a successful installation.
Because the Vault Server installation relies on IIS and MS SQL, the options you choose during installation must be compatible with your specific IIS and MS SQL configurations. In addition, certain system requirements must be in place before you install Vault. The installation guide will help you determine the right options for your system.
- Upgrading Vault Server
- Overview
- What the Installer does
- Pre-Installation Checklist
- Welcome to the Vault Server Installer
- Software License Agreement
- Read Me
- Setup Details
- IIS Process Model
- Ready to Install
- Troubleshooting Vault Installation Issues
NOTE: These instructions describe Vault Professional Server installation, but also apply to Vault Standard. The difference in Vault Standard installation is that Vault Standard does not have an sgdragnet database or VaultPro virtual directory.
Upgrading Vault Server
If you are upgrading an existing Vault Pro or Fortress server, back up your databases before beginning the installation.
If you have Fortress or Vault Pro 5.x, back up the sgvault, sgdragnet, and sgmaster databases. Before upgrading VaultPro 6.0 and later versions, back up the sgvault, sgdragnet, sgmaster, sgnotify and sgvaultindex databases.
You can back up the databases with SQL Server's backup tools, or use the Backup feature in the Vault Pro/Fortress Admin Web Client.
After backing up the databases, run the Vault Pro upgrade over your current installation. The Vault Professional installer will upgrade the Vault Pro/Fortress database in MS SQL Server.
If you're upgrading from Vault Standard to Vault Professional, you should back up - but not delete - your databases before installing Vault Professional. You must uninstall Vault Standard before installing Vault Professional. Click here for additional details on upgrading from Vault Standard to Vault Professional.
NOTE: Users with versions that are more than two versions out of date should upgrade in stages. See the Vault Upgrading Guide.
Overview
Before installing the Vault Server, verify that your system meets the requirements posted on the Systems Requirements page. Another resource that shows what Vault is compatible with is our Compatibility Chart.
In general, you would install the 64-bit version of the Vault Server on a 64-bit OS. However if your OS is 64-bit, IIS can be configured to run 32-bit apps so that you can install the 32-bit Vault Server. The 32-bit Vault server is required for VSS Handoff, which imports the latest version of a VSS database.
What the Installer does:
During the installation, the Vault server installer will:
- create the VaultService, VaultPro and SgDav directories on the local hard drive
- create or update the sgvault, sgdragnet, sgnotify, sgvaultindex and sgmaster databases in SQL Server
- create a SQL Server login and database user for the databases
- create the Server's web.config file for IIS
- give the Microsoft.NET Process account access to certain directories on the Vault Server Machine
- create the VaultService, VaultShadowFolder, VaultPro, VaultIndexService, VaultNotifyService and SgDav (Vault WebDAV) virtual directories in IIS, and their corresponding folders under the IIS web root
Pre-Installation Checklist:
Internet Information Services
Verify that Windows Internet Information Services (IIS) is installed with the additional features or roles:
- Static Content, found under Common Http Features
- ASP.NET 4.5 (or higher), found under Application Development
- .NET Extensibility 4.5 (or higher), found under Application Development
See http://support.sourcegear.com/viewtopic.php?t=10069 for additional details.
Microsoft Sharepoint Issues and applications that alter the root web.config
Sharepoint and Vault Professional cannot successfully co-exist on the same server machine without special configuration. Any other application that also makes changes to Vault's web.config file will require the same solution. If a website or application adds a web.config file in the same path that Vault occupies, then Vault will try to read that additional web.config file. For that scenario either the additional web.config will need to be removed or Vault will need to be installed to a different location.
Privileges
Please note, to install the Vault Server, you must be logged into Windows as a domain or local machine Administrator. In highly secure environments, users may need to launch the installer from an Administrative command prompt to get the necessary rights. To do so:
- Start a command prompt with Administrative elevated privileges
- Next, run \_> msiexec /i "\full\path\to\vault\installer.msi"
- Finally, verify SQL Server is running and that the Vault Server installer connects in a manner granting it SQL Server's sysadmin rights in order for the installer to make changes for the Vault related databases
Know your Options
During the installation you will be asked to choose certain options:
You will choose to install Vault to the IIS Default website or to a secondary website (if available) on the server machine.
You will decide which user\login will have access to the Vault virtual directory. Your choices are the machine account: Network Service or IIS APPPOOL\VaultAppPool account, or you can create a custom account. In most cases you will select the machine account. On newer Windows operating systems, if you will be using a custom account, you may have better results by launching the installing from an administrative command prompt.
Database Authentication
You will decide whether to use Windows Authentication or SQL Server Authentication for access to the Vault databases by the Vault process. Be sure your SQL Server is set up to accept the type of authentication you choose.
The options you select in the IIS Process model and SQL Server Setup screens determine what user has access to the Vault database. Examples:
Using Windows Authentication:
This describes using the IIS APPPOOL\VaultAppPool account, but applies to any of the IIS Process model selections.
If you select Windows Authentication during the SQL Server Setup portion of the installation, the installer will use your Windows credentials to log into SQL Server. The installer will create or update the sgvault, sgdragnet, sgnotify, sgvaultindex and sgmaster databases.
The Vault installer will also create or update the SQL Server login for the IIS APPPOOL\VaultAppPool account, and will create a role for the user IIS APPPOOL\VaultAppPool within the databases.
Using SQL Server Authentication:
If you choose to use SQL Server Authentication in the SQL Server Setup screen of the installation, enter the name and password of the SA user (or equivalent account) and the installer will log into SQL Server with those credentials.
Note: you are not creating a SQL account in this screen. You are providing a username with SQL Server administrative privileges (the SA account, for example) so that the Vault installer can make the necessary changes to the database. The Vault Server installation will use the SA credentials to create (or update) the sgvault, sgmaster, sgnotify, sgvaultindex and sgdragnet databases.
The Vault Server installer will also create a SQL login named 'sgvaultuser', and grant it access to the new databases. The SA account is used only during the installation process. After installation, Vault server will use only the sgvaultuser account to access the databases.
If SQL Server is on another machine:
The easiest way to install the Vault Pro Server when SQL Server is located on a different machine is to use SQL Server authentication.
However, if your SQL Server is on a different machine, and you want to use Windows Authentication, then the account you choose for the IIS Process Model should not be the machine account, as that only exists on the local machine. In this case, choose a custom account. The custom account needs to be a Windows account which has access to both the SQL Server and the IIS Server, usually a DOMAIN\USER account.
Document your selections for future upgrades.
The upgrade will look the same as your initial installation, but some parts will be filled in already. So that you are prepared for future upgrades, it is recommended that you document the choices you made for your initial installation. If you don't have this information, you can find information in the vault_install.log found in %temp% or in the Vault web.config files.
Welcome to the Vault Server Installer
Double click the Vault Install .msi file to launch the Vault Server Installation Wizard.
Click Next to continue.
Software License Agreement
Please read the license agreement. Select "I accept this agreement."
Read Me
Please read the notes concerning the version of Vault being installed.
Click Next to continue.
Setup Details
This screen gives you the option of choosing a Typical or Custom setup. The "Custom" option allows you to choose the Vault installation directory; Typical chooses the install location automatically, generally C:\inetpub\wwwroot.
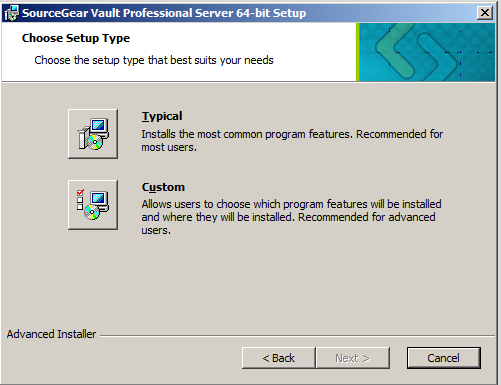
Choose Typical unless you have a specific need to install Vault in a non-standard location.
If you choose "Custom", the next screen will include a Browse button which allows you to choose a Web root folder other than the standard C:\inetpub\wwwroot.
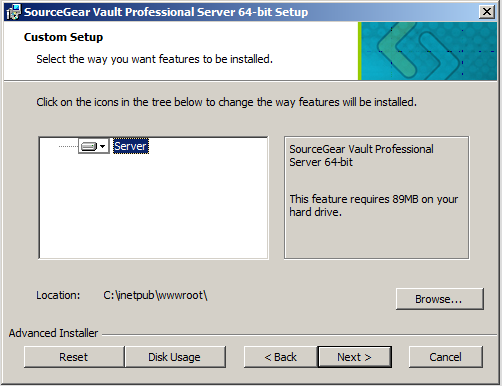
When you are satisfied with your choices, click Next to continue.
IIS Process Model
This setting determines the Windows Account that will receive permissions to the Vault Service physical directory, selected in the previous step. The default account for the IIS Process model is the Machine account, which is a local account. By default the path is C:\inetpub\wwwroot\VaultService.
If you want Vault to connect to SQL Server through Windows Authentication, the account selected for the IIS process model will be granted access to the database. For instance, if you select the IIS APPPOOL\VaultAppPool login, will be granted a login to SQL Server and the IIS APPPOOL\VaultAppPool account will be added as a user to the Vault databases, with the roles of public and db_owner.
If you want to connect to SQL Server through SQL Server Authentication, the Vault Server installation will create an 'sgvaultuser' SQL Server login account, which will be used by Vault to connect to the database. See the SQL Server Setup section for details.
There are two choices for the IIS Process model:
- Machine account, IIS AppPool.
The AppPool IIS ProcessModel account is created during the installation of the Microsoft.NET Framework.
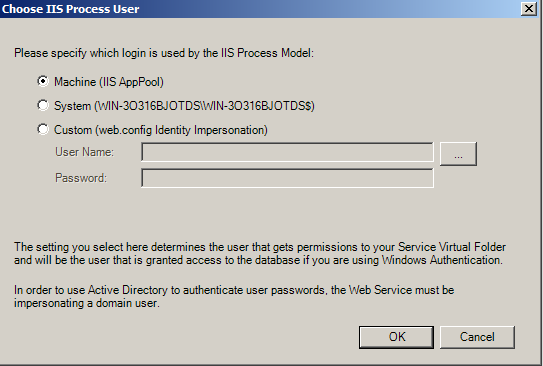
- Custom Account
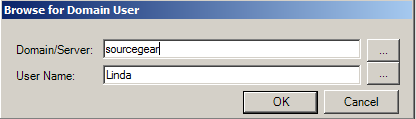
The Custom option allows you to specify a local or domain Windows user for the IIS Process User. Use a custom account when SQL Server is located on a different machine than the Vault Server, and you want to use Windows Authentication to connect to SQL Server. You should use an account which is accessible by both machines - specifically a domain account - DOMAIN\USER.
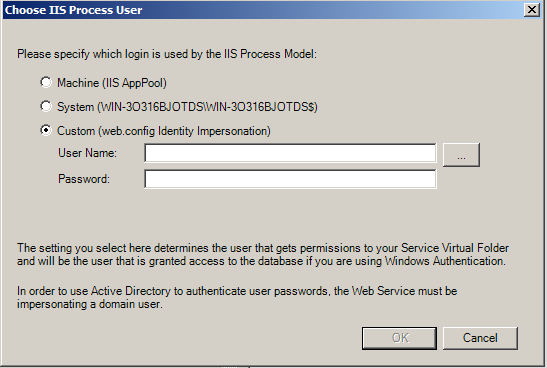
You must use an existing Windows account.
Ready to Install
The Vault server installer will now update your system. The Vault Server Configuration Status dialog shows the status of the configuration, step by step.
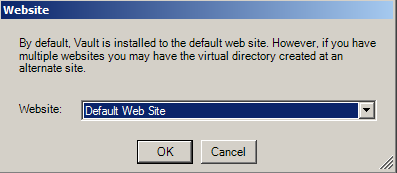
Updating System - Web Site
The first step is installing the Vault virtual directory. By default, Vault is installed to the IIS Default Website. However, the Vault installation program will detect whether you have more than one website configured. If you do not want the virtual directory installed the Default Web Site, make a selection from the other web sites listed in the combo box.
Vault Administration
Create a password for the Vault Admin user.
Vault can accept a blank password, but this is not recommended for security reasons.
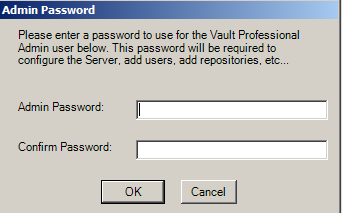
Click OK to continue.
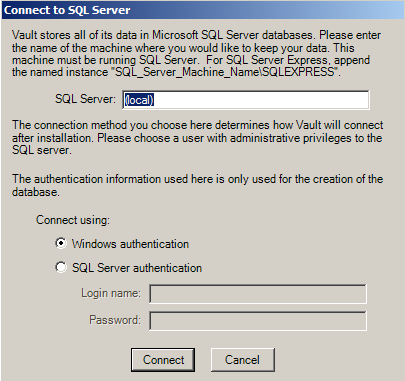
SQL Server Setup
Specify the location of the SQL Server which will store the Vault databases, and the authentication method the Vault Server should use to connect to the database. SQL Server can be on the same machine as the Vault web service, or SQL Server can be on a different machine, but on the same network. Your SQL Server could also have multiple instances installed on the same machine. You may have to enter the instance name in the form of ServerName\InstanceName. Please verify SQL Server is running before you complete this step.
The Vault Server can connect to SQL Server via Windows Authentication or SQL Server Authentication. If you choose SQL Server Authentication, please verify SQL Server is set up to allow SQL Server Authentication
When installing Vault Server with SQL Server Express, use ".\sqlexpress" or "machinename\sqlexpress" instead of (local) for the SQL Server name, since SQL Express is installed as an instance.
If you select Windows Authentication, the account of the logged in Windows user who is running the Vault installer must be a full SQL administrator. The installer will not prompt for alternative Windows Authentication credentials.
Vault installer will grant database access to the user specified in the IIS Process Model screen.
If you choose SQL Server authentication, you must enter credentials for the SA account or another account that can create or modify the databases. The account must also be able to create logins and users to establish the connection between the Vault Service and the sgvault/sgmaster/sgdragnet/sgnotify/sgvaultindex databases.
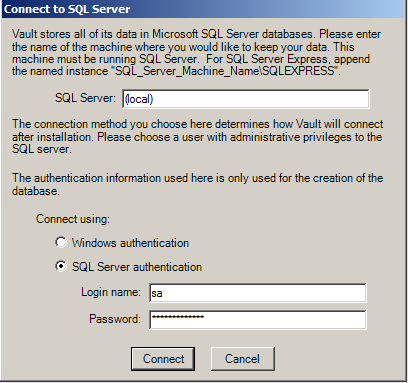
Note that the SA account or equivalent account is only used once during installation to create the databases and appropriate user and logins for the Vault.
If you chose SQL Server authentication, the Vault Installation creates a SQL Server login named 'sgvaultuser', and grants this account access to the 'sgvault', 'sgdragnet'. 'sgnotify', sgvaultindex' and 'sgmaster' databases. Sgvaultuser will have db roles of public and db_owner. Vault is set up so that only sgvaultuser can access the Vault database.
Click Next to continue.
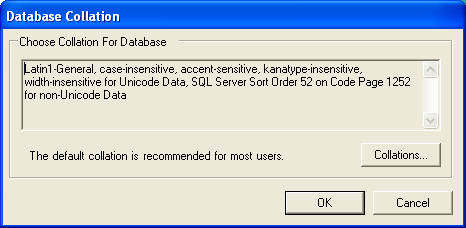
Database Collation
Choose Collation for Database. This dialog appears when there are no existing databases. The collation determines how the database sorts text strings in the database, based on the language used. The Vault installer chooses a collation that is appropriate based on the language settings of the machine. If you wish to choose a different collation, click Collations... and select the one you want.
Updating System Status
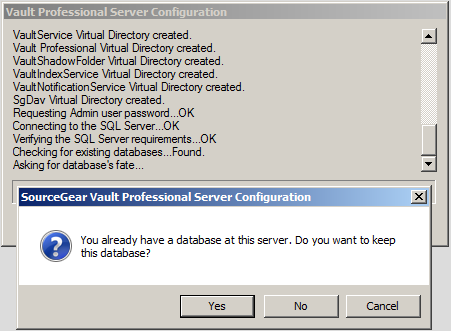
The Vault server installer will check to see if Vault databases exist.
If you re-install Vault and databases already exist, you will be asked if you wish to keep the existing databases or drop the databases and create new ones. If you choose to drop the databases, a confirmation box will appear.
If you are upgrading from Fortress or Vault Standard to Vault Pro, a similar prompt will appear. You should choose to keep and upgrade the existing databases.
Installation Complete
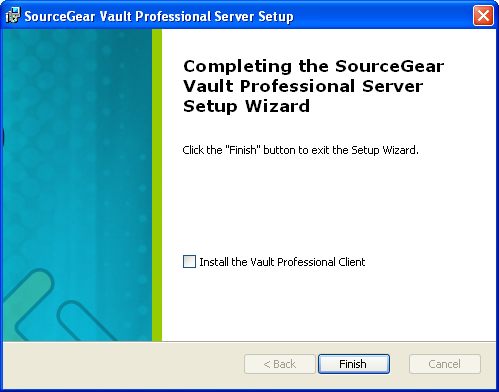
The server installation is complete when the status message says "Completing the SourceGear Vault Professional Server Setup Wizard." If you wish to install the Vault Pro Client, check the "Install the Vault Professional Client" checkbox before pressing OK. The client installer will begin.
Vault's Admin web site will launch.
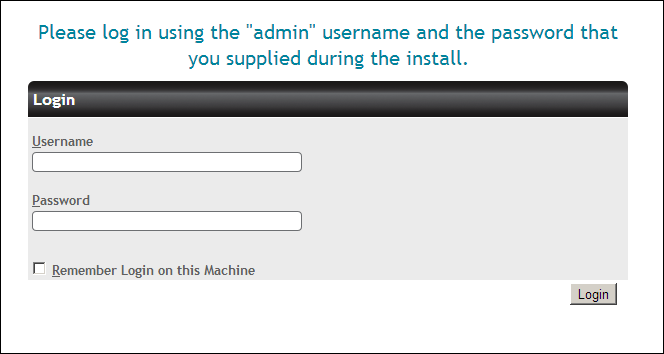
Enter the username and password you chose in the Vault Administration dialog during the installation. Vault is now installed and ready for you to add license keys.
Troubleshooting Vault Installation Issues
If you are unable to connect to the Vault Server after installation, review Vault installation Help and search the SourceGear Support Forum at support.sourcegear.com.
If you are unable to resolve the problem, contact Technical Support, support@sourcegear.com. Please provide copies of any error messages, plus the following information, as relevant.
- Vault Pro installation log
If you had an unsuccessful installation, we would like to see the Vault Pro installation log. It is named vaultpro_install.log and should be found in your temp folder as defined by the USER's TEMP Environment variable. If you type %temp%, in a browser address bar, it will open your temp folder.
- Web.config file
Web.config is located in the inetpub\wwwroot\VaultService directory (or under the location you chose during a custom installation). This file is helpful in troubleshooting installation and database access issues.
- Vault Pro Server log
If you are experiencing problems with Vault Pro operations, the log file will help us determine the problem. In the Vault Pro Server Admin Web Client under Server Settings, set the Log Level to Debug, perform the actions which are failing, then send a copy of the sgvault.log file to Technical Support. The default location of the sgvault.log file is in the %WINDIR%\Temp\sgvault folder.
Be sure the set the logging back to Quiet mode, as debug logging can use significant disk space.